In this link you can access more information in the Application Note: [USB Braille Machine](https://docs.google.com/document/d/1HlL_t_NP2DlqpAy3oB2dQpBOwnB3AoPr9fjIHCdc0V0/edit?usp=sharing)
# Implementation This digital Braille Machine is projected using the ChipInventor platform and implemented on the Tang Primer 20K FPGA. The project utilizes 8 buttons and 2 switches of the Devboard to convert Braille combinations into standard keyboard outputs using USB HID (Human Interface Device) functionality, allowing seamless integration with computers without additional drivers. The following table outlines the key specifications of the project and its hardware requirements: **Table 1 – System Specifications**| Field | Description |
| FPGA Board | Tang Primer 20K |
| FPGA Core | Gowin GW2AR-18 |
| USB Functionality | HID (Human Interface Device) – Recognized as a keyboard |
| Input Interface | 6 Braille buttons + function keys (Caps Lock, SpaceBar button, Delete, Number Mode) |
| Braille Standard | International Braille (Unified Standard) |
| Supported Characters | Uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers |
| Unsupported Characters | Special symbols and punctuation marks |
| Clock Frequency | 27 MHz |
| Button reading interval | 1 second |
| Power Supply | 5V via USB-A |
| Programming Interface | JTAG or USB Programmer |
The project is based in [Internationally Standardised Braille](https://www.pharmabraille.com/pharmaceutical-braille/the-braille-alphabet/).
Here is the blocks diagram of this project: [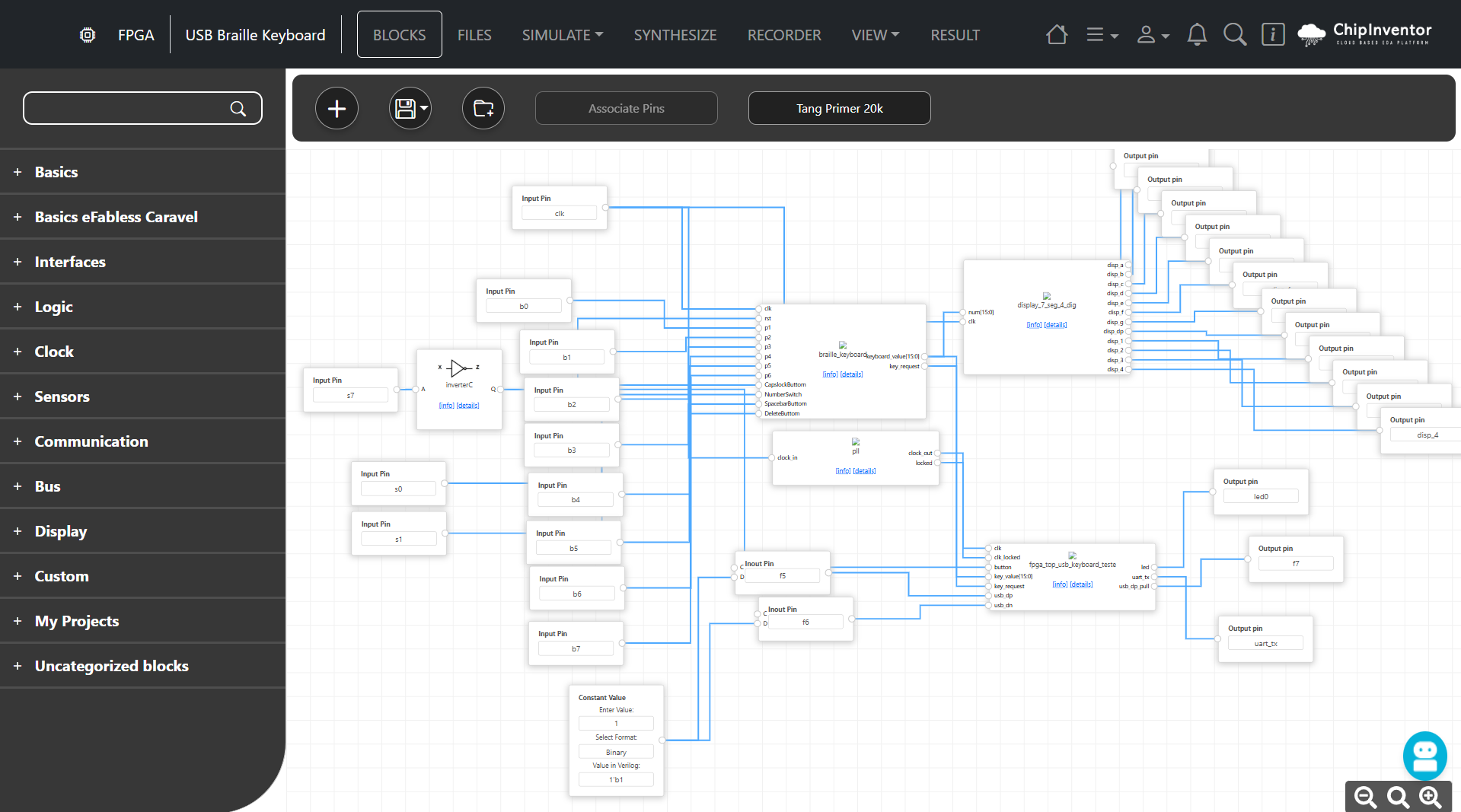](https://design.wiki.chipinventor.com/uploads/images/gallery/2025-08/bXfTlBA43GaaL8zN-image2.png) # Visual Resources [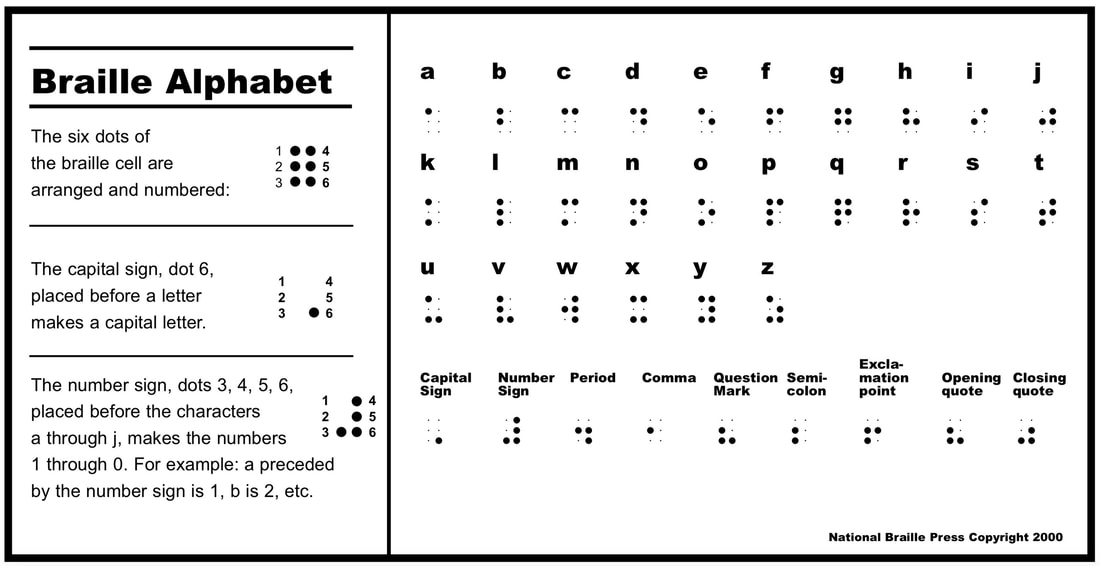](https://design.wiki.chipinventor.com/uploads/images/gallery/2025-08/Ysiz2eLU3y3GWVR8-image5.png) **Figure 1 – Internationally Standardise Braille dots arrangement** [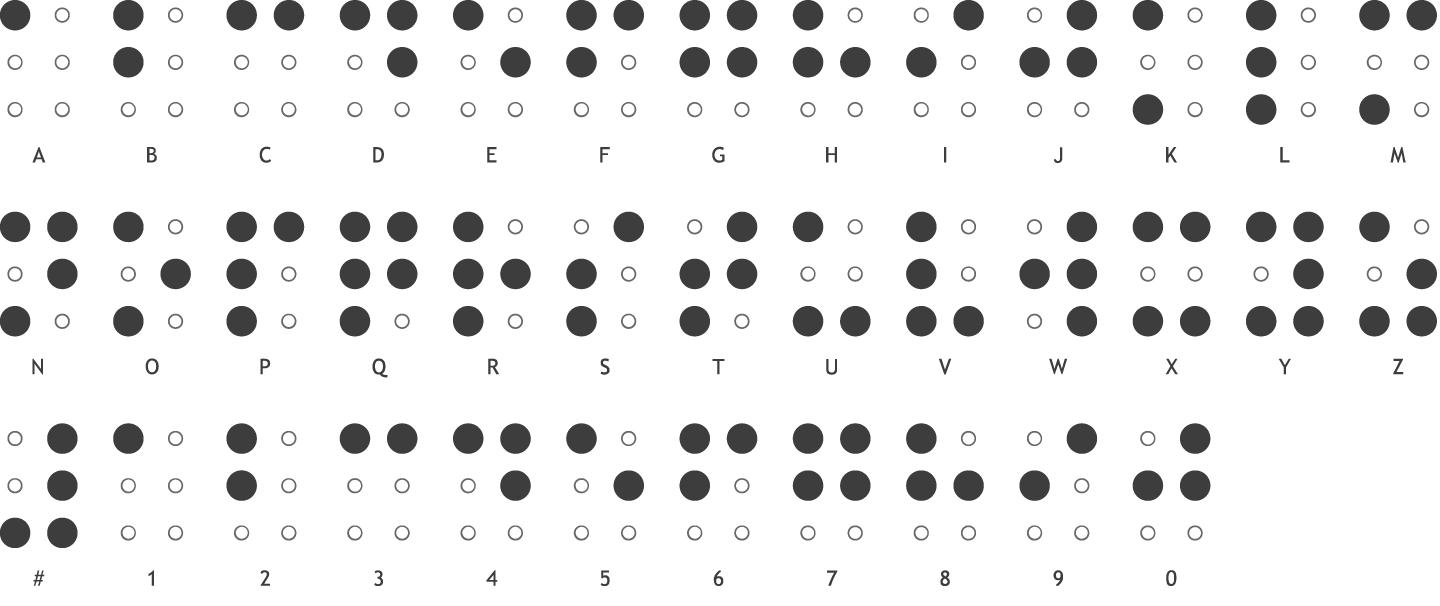](https://design.wiki.chipinventor.com/uploads/images/gallery/2025-08/qXgxXeYRxupAezep-image3.png) **Figure 2 – Internationally Standardise Braille alphabet and numbers** [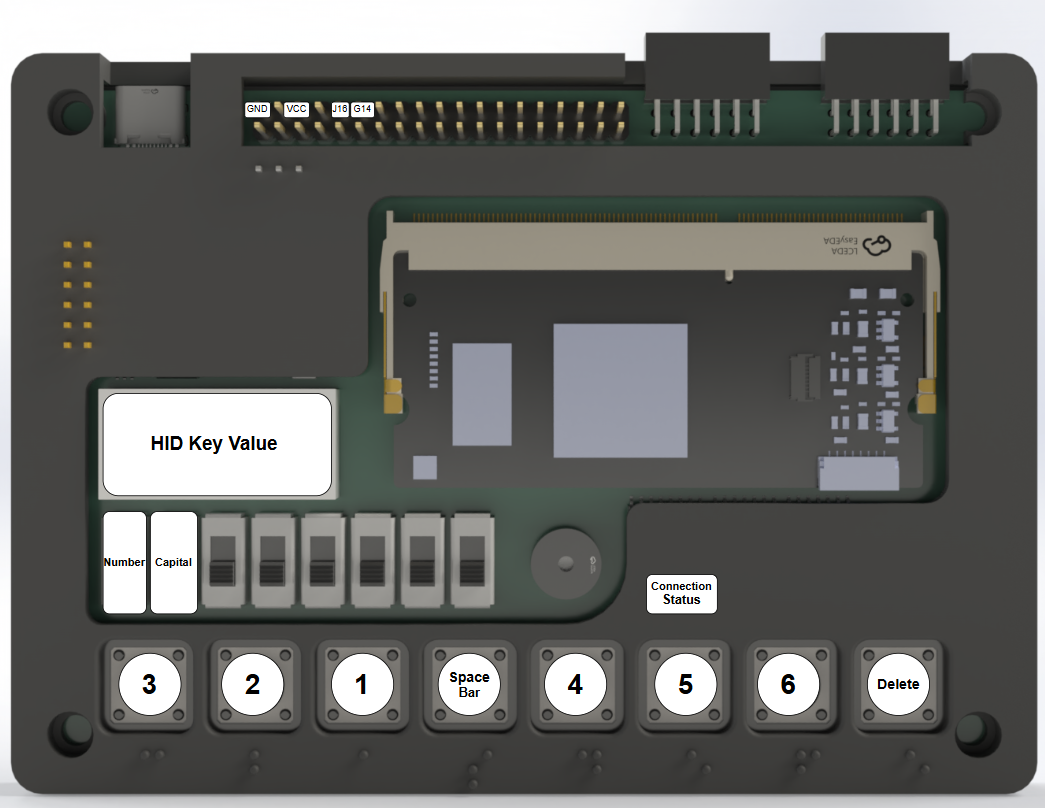](https://design.wiki.chipinventor.com/uploads/images/gallery/2025-08/iR31TPQer43k3X1Q-image1.png) **Figure 3 – Input keys placement** [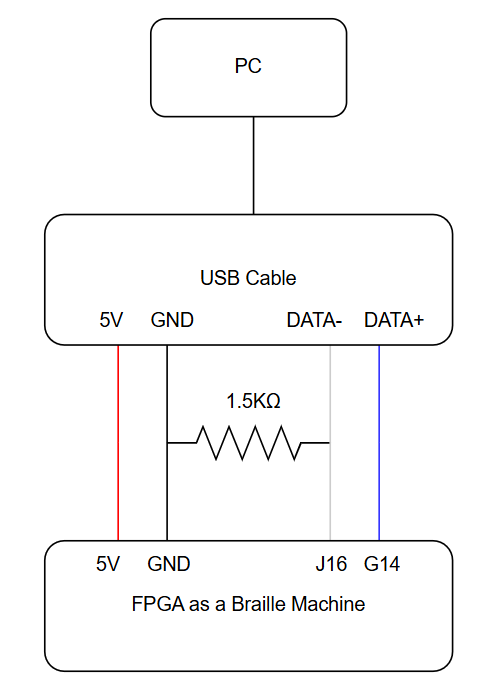](https://design.wiki.chipinventor.com/uploads/images/gallery/2025-08/cN4whpoSXY3BXoAH-image4.png) **Figure 4 – How to connect**